The thought of having to have an endoscopy is not a pleasant one and the reality can be even worse. Due to the pain usually caused by this all too often essential procedure it is normally necessary to have a sedative, but even sedated patients can report extreme discomfort.
Diagnostic colonoscopy with video detection of polyps
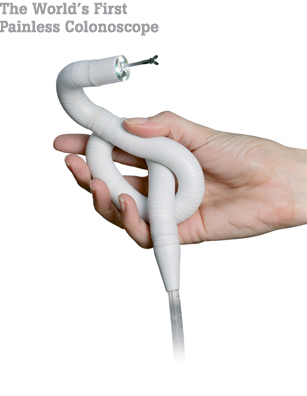
It therefore comes as a great relief to learn of a new 'painless colonoscopy' device that senior Consultant Gastroenterologists such as Dr Premchand operating colonoscopy clinics are starting to put into practice. The new self-propelled device was developed in Italy and is called an 'Endotic System' or ES. The advanced flexibility reduces stretching within the gut and allows the probe to move smoothly through the colon without interfering with areas such as inflamed regions, folds of membranous tissue such as mesenterics or growths such as polyps. 
Furthermore, the 'Painless Colonoscope' only uses a minimal amount of forced air, as required for diagnosis. The result being a pain-free diagnostic procedure. According to the World Journal of Gastroenterology, "The ES allows the visualization of the entire colonic mucosa in most patients, with good sensitivity/specificity for the detection of lesions and without requiring sedation."
No need to share
The new colonoscopy Endotic System is also disposable and this is very welcome news. As reported in the BMJ, "Endoscopy itself is not dangerous, but the current cleaning process used between procedures leaves patients susceptible to infection and troubles many healthcare practitioners." Referring to a 2013 study where Forbes go on to comment, "It was found that 15% of endoscopes for the stomach, colon and duodenum were still contaminated after many complex cleaning processes. Every time you undergo an endoscopic procedure, you share an endoscope with someone else, and unfortunately, a germ-free instrument is not guaranteed although it may be assumed".
Dr Premchand says that in his experience with the new Endotic System there is the potential to reduce a huge amount of discomfort and the disposable nature of the devices means that colonoscopy can now be both safe and painless.
Robots designed by Mother Nature
The Endotics System is CE-marked for diagnostic colonoscopy. Development came about as the result of research into robotic biomimetics which is the application of biological methods and systems found in nature to the study and the design of robotic systems.
Sequences of actions are implemented to move the probe with a form of motion similar to that of an inchworm. The manufacturers claim that, "This kind of locomotion, is particularly suited to an unstructured environment like the intestine". The sterile, disposable probe (or E-Worm) has a head, a steerable tip, a flexible body, a thin tail (7.5 mm in diameter) and a special tank with an electro-pneumatic connector. The head contains a camera and light sources plus channels for water jet and air. The probe is controlled via a hand-held console allowing the doctor to steer the head of the robotic colonoscope in every direction,