Main image: i-stock
Are you looking forward to being released from Lockdown and enjoying some socialising?
Perhaps, along with the yearning for chilled G and Ts and face to face chatter, you may be experiencing a certain amount of trepidation about coming face to face with people?
The long months we have spent indoors, has meant many of us have been focusing on the flaws and faults we see in the mirror – both real and imagined. Enquiries for cosmetic procedures have jumped by more than 500 per cent during lockdown. Patients realise this is an opportunity to recover at home, with no awkward questions from colleagues and bosses.
A spokesperson for the British Association of Aesthetic Plastic Surgeons spoke to The Times about the massive increase for services.
We thought the pandemic would knock everything but we have all been super busy. The only mitigating factor has been the facilities, because a lot of places have been taken over by the NHS. The main reason [for the high demand] is that people can recuperate at home, they don’t have to take sick leave and no one has to know.
So which are the best treatments to consider before lockdown ends?
Thermavein for facial redness
If it looks like you’re in a permanent state of embarrassment during your Zoom calls, you may be suffering from the skin condition Rosacea. This common skin condition causes redness and visible blood vessels in your face. There may also be small, red, pus-filled bumps, which are prone to flare-ups. Although Rosacea can be hidden using makeup or treated using medications and lasers, Dr Peter Finigan, of UK Vein Clinic, says a new treatment called Thermavein offers a safer option with good results. ‘Thermavein is a form of 'thermal coagulation', where a precisely targeted source of heat is used to seal, collapse, and gently remove your thread veins. It’s highly effective, and delivers far better outcomes than laser treatments, which risk discolouring or damaging your skin.’
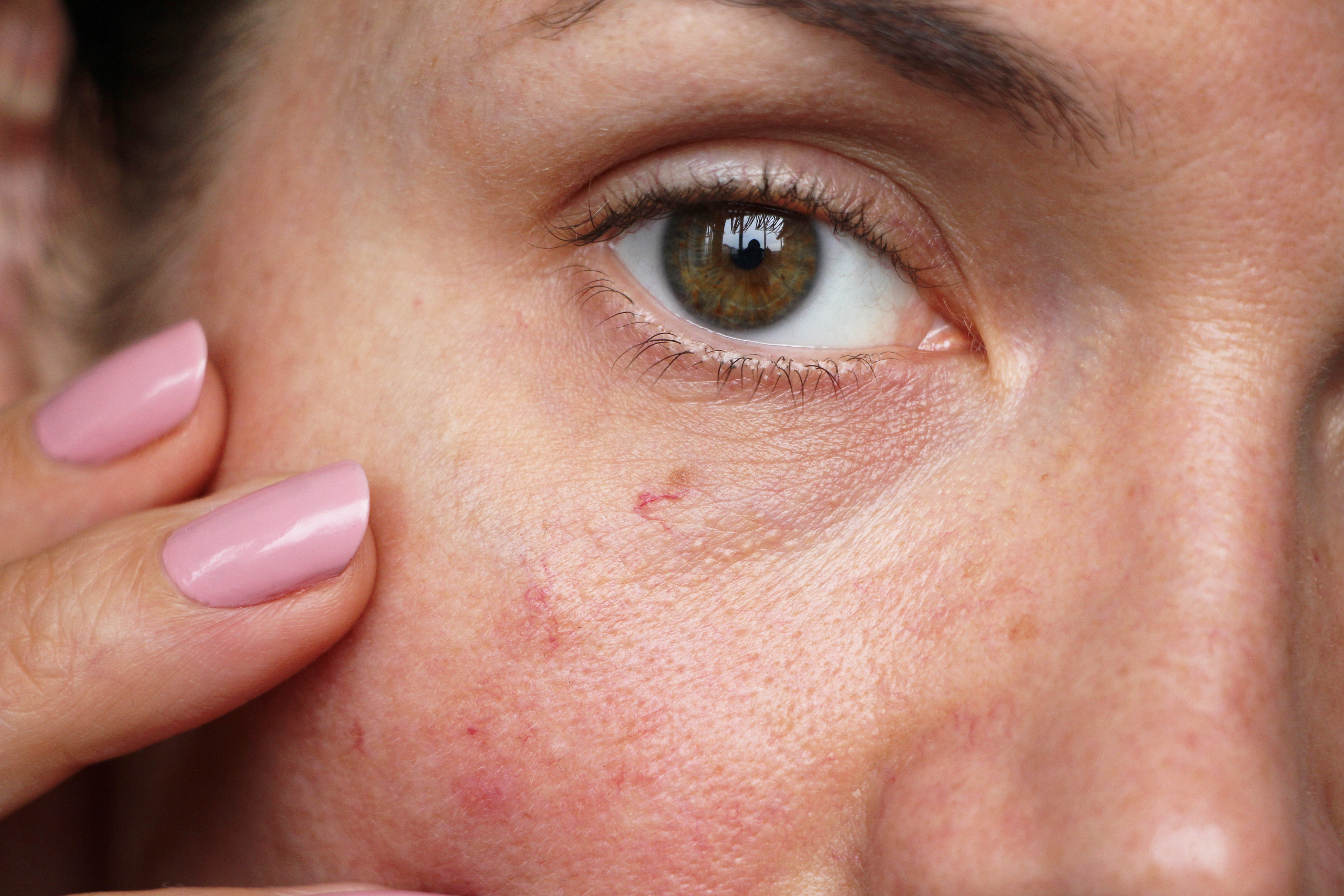
Image: Shutterstock
Micro Sclerotherapy for spider veins
In the cold snap we’re all dreaming of the hot weather and getting some sun – and a dose of much-needed Vitamin D – but if your skin isn’t creamy smooth, you may be less keen to shrug off the layers. Spider veins are small, damaged veins that can appear on the surface of the legs or face. They can be blue, purple, or red and may appear in the form of thin lines, webs, or branches. They’re not dangerous, but they can be confidence-sapping. Dr Peter Finigan, of UK Vein Clinic, says: ‘To treat thread veins in the legs and elsewhere, we often combine the Veinwave technique with Micro Sclerotherapy, a treatment option gently and permanently removes unhealthy veins by injection.’
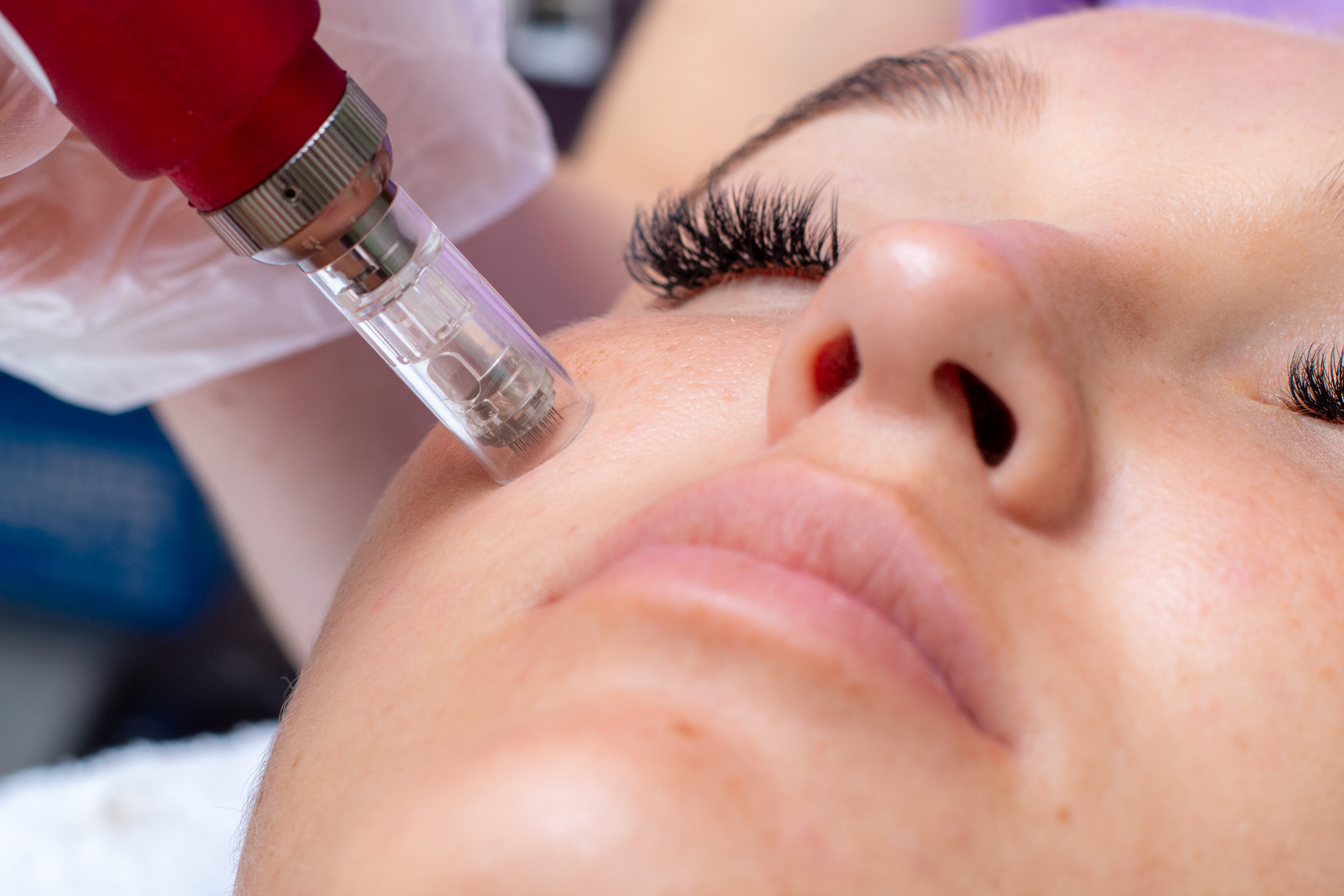
Image: Shutterstock
Micro-needling for tired, ageing skin
Many of us are noticing that lockdown seems to be making our skin age a bit faster. Research has found that over a quarter of women in the UK (27 percent) felt the lockdown period had accelerated the ageing process. According to dermatologist Dr Suchrita Badvey, micro-needling can help. This is a safe and effective way to rejuvenate skin and treat scars and wrinkles. It naturally helps trigger collagen and elastin synthesis within the skin with maximum results and minimum down-time. Micro-needling is safe for nearly all skin types. The technique works by creating microscopic channels in the skin while still keeping the epidermis intact. This process actively produces growth factors which induce collagen producing cells known as fibroblasts to produce fresh new collagen and elastin which are essential in keeping the dermis elastic and resilient thus firmer and wrinkle free and glowing. It may take up to two to three days to recover, depending on the extent of the treatment, and the results should last between four and six weeks.
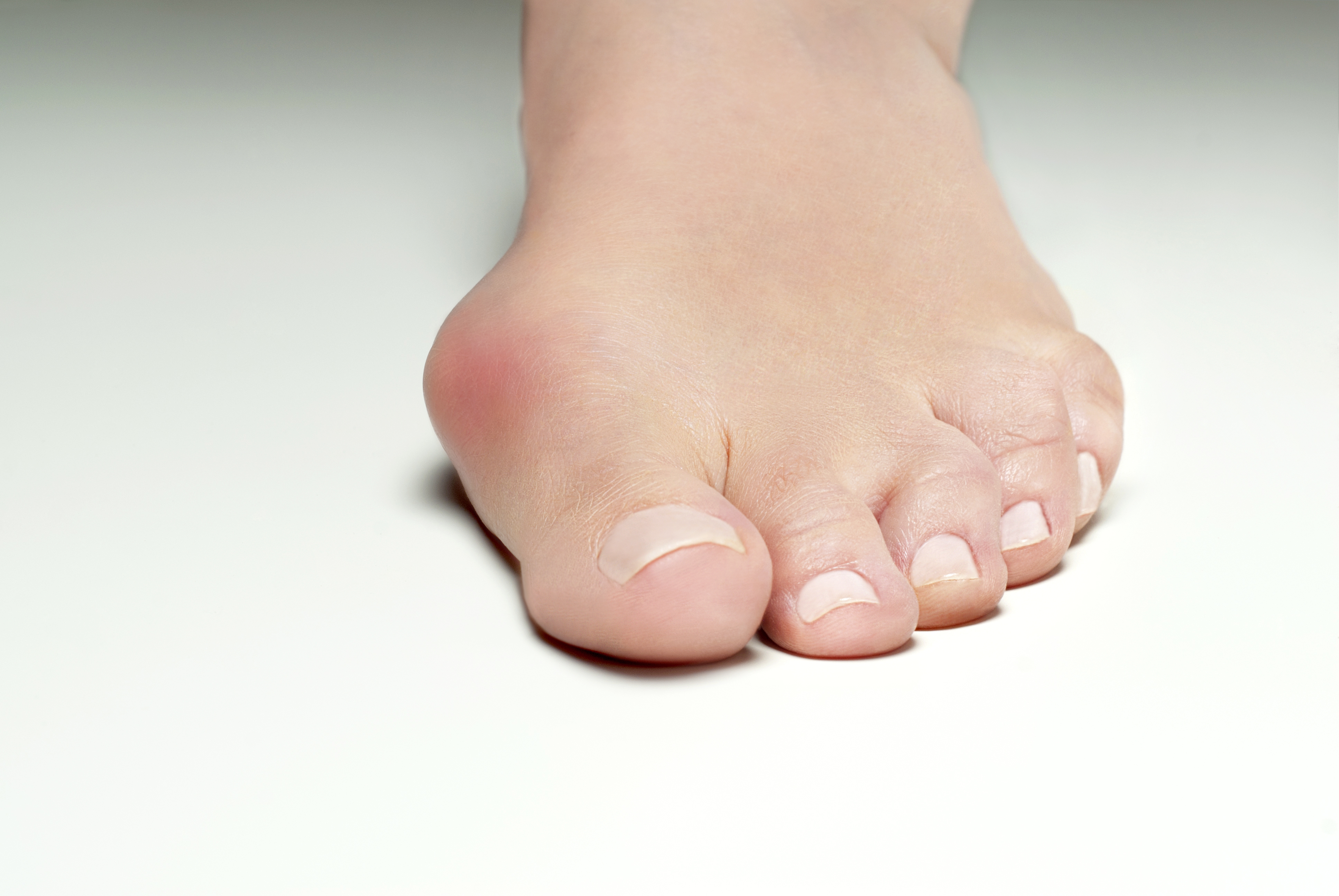
Image: Shutterstock
Bunion surgery for feet
If getting out of trainers and walking boots and slipping into strappy sandals is your goal, you’ll want to be bunion-free. Bunions are a deformity of the big toe joint, where a painful bony growth juts out on the joint at the base of the big toe, which forces the big toe to turn in at an angle towards the other toes. Not only does this problem cause issues with footwear and aesthetics, bunions can be very painful. Orthopaedic foot surgeon Mr Haroon Mann of The Royal Free NHS Trust says: ‘An advanced bunion may make your foot look deformed. If your bunion gets too severe, it may be difficult to walk. Your pain may become chronic and arthritis can develop.’
Although the operation to correct bunions can be carried out in a day under local or general anaesthetic, it may take a couple of months to recover. It could be a great idea to get this done now, allowing you to be bunion-free and all recovered when the world opens up again.
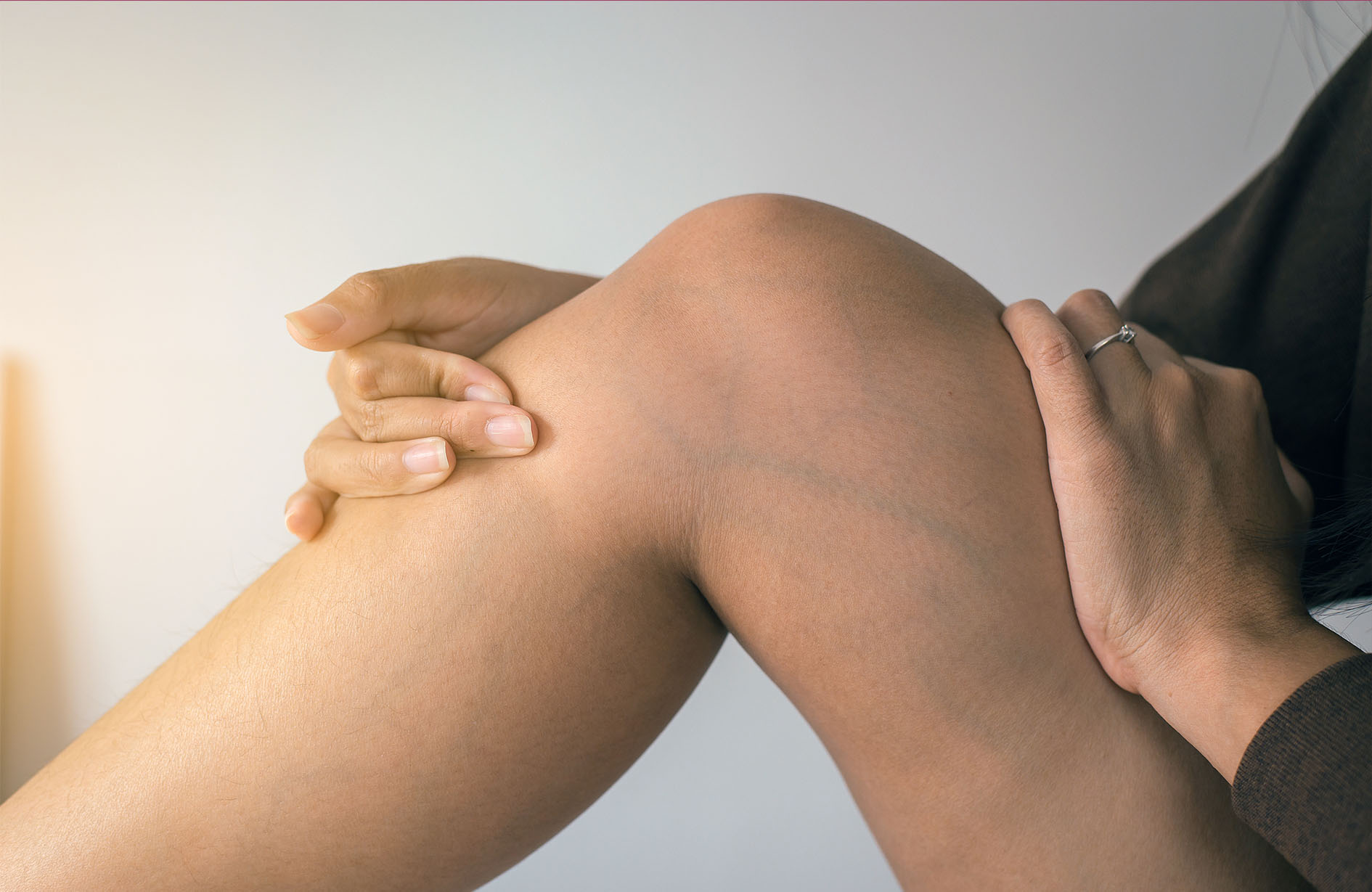
Image: Shutterstock
Radiofrequency treatment for varicose veins
Baring legs in summer is one of the great joys in life. However, for those who suffer from varicose veins, when the weather heats up, the cover-up act commences. These swollen and enlarged veins are often bluish in colour, and may look lumpy. Not only do they look unsightly, they can also feel heavy and painful. ‘Varicose veins occur when the valves are no longer functioning correctly and blood flow starts reversing (known as 'reflux') - causing a localised build up in pressure,’ explains Professor Stephen Black of UK Vein Clinic. ‘Reflux occurs when the failing saphenous vein valves actually snap, allowing blood to travel backwards with gravity. This condition is known as venous reflux disease or 'chronic venous insufficiency'.’ Clinical vascular scientist Mr Fabrizio D’Abate says new treatments are now available. ‘Radiofrequency treatment - a form of minimally invasive varicose vein surgery - is the best overall option. Unlike other surgeries, it can be completed under local anaesthetic, carries lower risks of scarring and post-op pain, and consistently delivers excellent results.’
Read more ...
- Why it's important to treat varicose veins
- Diagnosing and treating varicose veins accurately
- 7 dangers of sitting down too long






