Alex Reid strutted his stuff in Surrey this weekend, as he competed in the bodybuilding competition Mr Hampshire.
It’s fair to say he looked rather different to his appearance just three months ago.
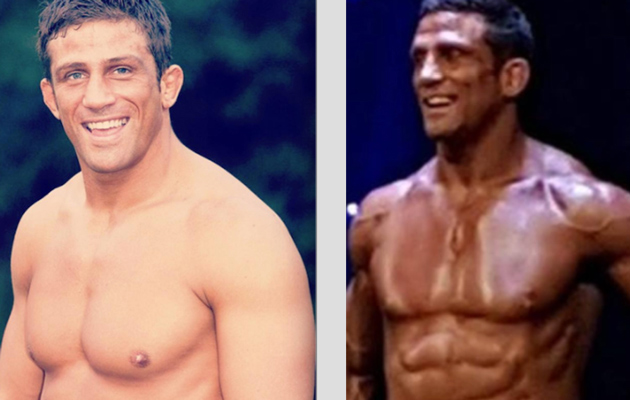

Bronzed, gleaming and totally ripped, he had lost 10% of his body fat after an intensive training programme. His weight remained the same. The fat has been replaced by muscle.
He revealed he shaped up in just 10 weeks for the competition.
In a caption on Instagram, he wrote: “Mr Hampshire today!
“I lost 10% bodyfat over 10wks!… #summerbody #goals #gettinginshape #motivated.”
So how did Alex – who is now 41 - manage to achieve this impressive feat?
These are Alex Reid's 3 secrets for shaping up.
1. Get a DEXA Body Composition Scan
The first thing Alex did was head to see Professor David Reid, a leading expert on DEXA (Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry) for a Body Composition Scan. DEXA scanners are used to check bone density, but certain models are equipped with ‘Advanced Body Composition’ capabilities and provide an extremely accurate indication of total fat in the trunk region. As well as being a useful tool for athletes and bodybuilders it’s also an important diagnostic marker of health in its own right. When fat accumulates here, doctors know this is a risk factor for diabetes, heart disease and cancer.
The scanner can even identify whether fat is stored around vital internal organs such as the liver, pancreas and intestines.
Prof Reid first scanned Alex in March. The second scan was on the 1st of June. Prof Reid told Alex after the second scan: “Your Body Composition results have changed considerably in the last 10 weeks. While your weight is unchanged your percentage lean (muscle) mass has increased by 11.6% since March and your percentage body fat has overall fallen from 16.3% to 7.4%.”
2. Diet
Alex also ate a protein-rich diet, eschewing his usual carb laden treats. He wrote: “I have been so hungry for carbs on my contest prep 4 Mr Hampshire…“#team #competition #topnutrition #hungry.”
If you wish to emulate Alex, visit a clinical and sports dietitian.
We spoke to Clinical and Sports Dietician Rick Miller what his advice would be to bodybuilders looking to shape up with more protein:
"A simple change in foods (such as Greek yoghurt in the morning with muesli and fruit, rather than plain breakfast cereal and milk) will help enhance the protein content of a meal."
He added: "After you've taken this step, fill in the gaps with a reputable brand of protein supplement. Always read the label carefully, take the recommended serving size and don't be tempted to take far more than is necessary, as this is not supported by the current evidence.
3. Try Non-Surgical Cosmetic Surgery
Alex Reid also tried non-surgical liposuction to make his body super-sculpted.
Alex added in a caption: “Body starting to get there thanks to diet/training & @danielmassage & his fantastic 3D-Lipo fat removing machine!”
Alex was obviously pleased with the results, but according to Mr Ash Mosahebi, consultant plastic surgeon and a spokesperson for BAAPS, it is better to see a properly qualified doctor for cosmetic surgery. He commented: “It does worry me a lot that some people are putting their health at risk by visiting unqualified therapists.
He said:
"Honesty and management of expectations is key, and commercial High Street clinics often don’t provide this, promising the unachievable to patients who have an unrealistic view of what can be done."